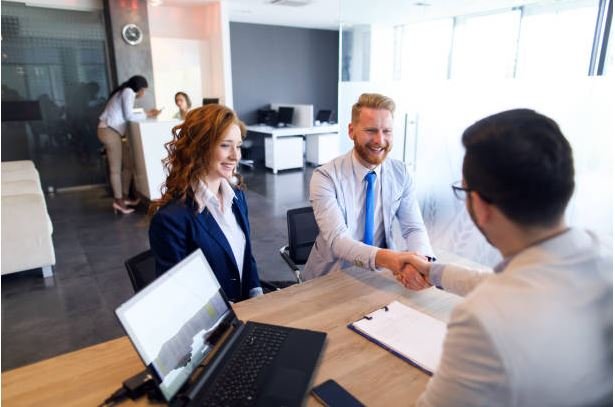
An interest rate refers to the amount of funds lenders charge their borrowers. It is expressed as a percentage of the principal or the amount of money loaned. Most lenders note their interest rate on an annual basis in APR (annual percentage rate). However, there are cases where lenders consider a borrower’s savings to get what is known as the annual percentage yield (APY). The APY is used to determine the earned interests in some of the deposits made by borrowers. Therefore, lenders use different calculators to compute their interest rates.
But where do lenders get these calculations from? Do not worry. Scroll down the article, and you will get everything you need to know about the analysis of these interest rates.
Understanding Interest Rates
Lenders also define a loan interest as the charge to the borrower for using a particular asset. Funds in a business fall under the category of current assets. Therefore, taking a loan means using an asset that you will later return to the owner. However, since the owner is in business, they will charge you a few funds known as interest. For all loans, the interest rate is applied to the principal. In other words, the loan charges are directly proportional to the loan you apply for. This means that if you take a loan of $10000, your lender will use a certain percentage to calculate the amount of funds you will pay after a specified period. The amount will be higher than a person who borrows $5000. You need to understand that different banks or financial institutions use different interest rates to calculate the number of funds to charge their borrowers.
How are rates determined in a Financial Institution?
Various factors determine the interest rates that different banks and financial institutions charge. In most cases, a central bank in a state can set an interest rate that ought to be used to charge borrowers. Commercial banks use these rates to determine the APY range to assess their borrowers. In most cases, banks will use a slightly lower rate to win the confidence of their clients.
Inflation Rate
The inflation rate also helps in determining the interest rates to be charged in loans. In most cases, when the inflation rate is high, banks tend to set higher reserve requirements, tighten money supplies, and ensure a tremendous demand for credit. With increased interest, people will save more and avoid taking loans. Fewer funds will be available in the economy, and the inflation rate will reduce in the long run. Therefore, to facilitate higher inflation rates, commercial banks in a state usually set higher interest rates to discourage people from borrowing.
In the end, you need to understand that the interest rates charged on your loan depend on your lenders. Although the central bank in a state can determine the rates to be used when issuing loans, the final decisions remain in the hands of your lenders. Other aspects that determine these rates include the inflation rate in a nation.