Introduction:
VSM Best Practices Value Stream Mapping (VSM) has emerged as a powerful tool for organizations seeking to enhance efficiency, minimize waste, and improve overall performance. Originally rooted in lean manufacturing principles, VSM has evolved to encompass various industries, including healthcare, finance, and technology. To unlock its full potential, it is crucial for businesses to adopt best practices that align with their specific needs and objectives. This article explores the key VSM best practices and offers insights into how organizations can leverage them to achieve operational excellence.
- Understand Your Value Stream:
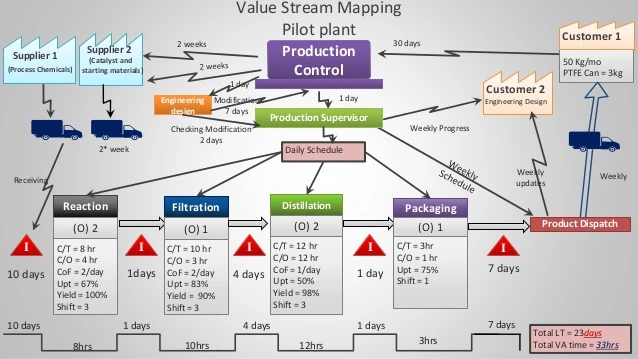
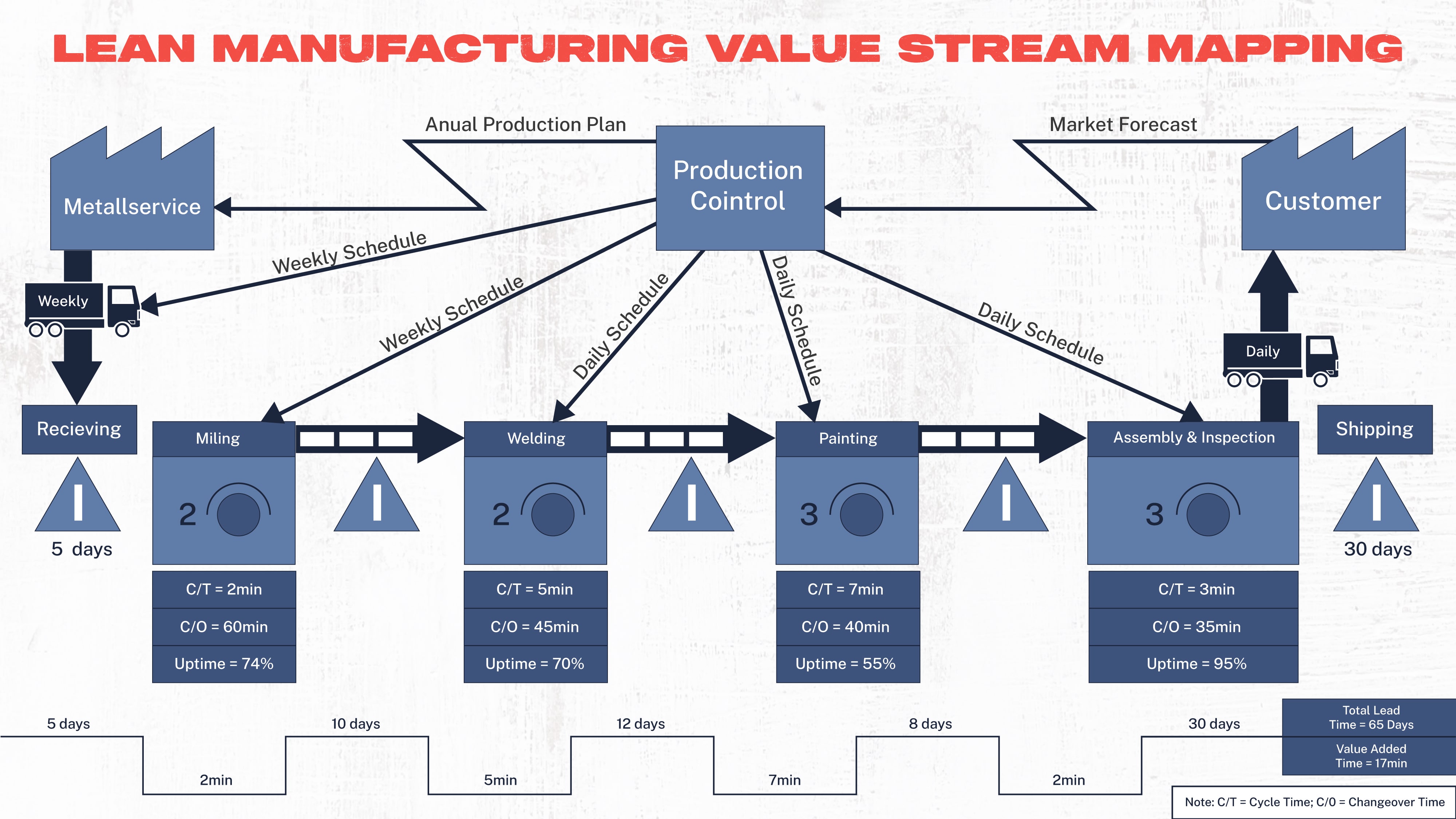
Before embarking on a VSM initiative, it is imperative to have a comprehensive understanding of your organization’s value stream. This involves mapping out the entire process, from raw materials to the delivery of the final product or service. Take into account every step, handoff, and interaction involved in the value creation process. This foundational knowledge serves as the basis for identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Collaborative Cross-Functional Teams:
Successful VSM implementation requires collaboration across different departments and functions within an organization. Establish cross-functional teams that bring together individuals with diverse expertise. This collaborative approach ensures a holistic understanding of the value stream and facilitates the identification of bottlenecks and waste. Regular communication and shared insights are crucial for the success of the VSM process.
Must Read= Understanding Everything About Bitcoin Fintechzoom Before Investing
- Define Clear Objectives and Scope:
Clearly define the objectives and scope of your VSM initiative. Determine the specific goals you aim to achieve through value stream mapping, whether it’s reducing lead times, improving quality, or enhancing customer satisfaction. Establishing clear objectives provides a roadmap for the entire VSM process and helps measure the success of the improvements made.
- Focus on Customer Value:
The essence of VSM lies in understanding and maximizing customer value. Identify and prioritize activities that directly contribute to meeting customer needs and expectations. By aligning processes with customer value, organizations can eliminate non-value-added activities, streamline operations, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.

- Gemba Walks for Real-Time Insights:
Gemba, a Japanese term meaning “the real place,” emphasizes the importance of observing processes in their actual work environment. Conduct Gemba walks to gain firsthand insights into how work is performed. This direct observation allows teams to identify inefficiencies, understand variations, and collect real-time data critical for accurate value stream mapping.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
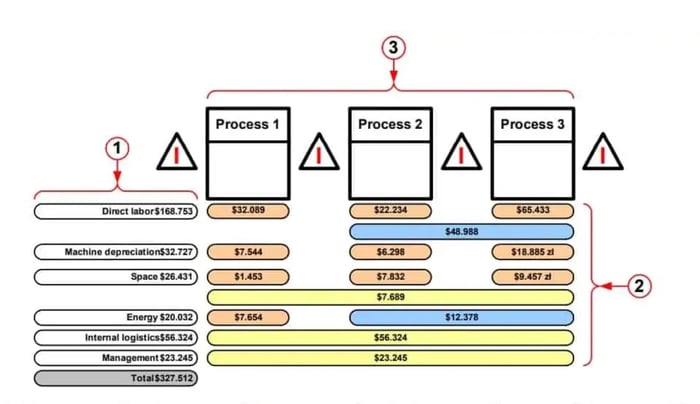
Utilize data to drive decision-making throughout the VSM process. Collect relevant metrics and performance indicators to quantify the current state of the value stream. Analyze this data to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement. Data-driven decision making ensures that improvements are targeted and impactful, leading to sustainable enhancements in the value stream.
- Kaizen Mindset:
Embrace a Kaizen mindset, emphasizing continuous improvement. VSM is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that requires a commitment to constant refinement. Encourage employees at all levels to contribute ideas for improvement, fostering a culture that values innovation and adaptability. Regularly revisit and update value stream maps to reflect the evolving nature of the business environment.
- Visualize the Value Stream:
Effective visualization is at the heart of VSM. Create clear and concise value stream maps that provide a visual representation of the entire process. Use standardized symbols and colors to highlight different elements, making it easy for team members to understand and analyze the information. Visualizing the value stream promotes transparency and aids in the identification of improvement opportunities.
- Set Realistic Timelines:
When implementing VSM, set realistic timelines for achieving improvement goals. Rushed implementations may lead to oversights or inadequate analysis, undermining the effectiveness of the process. Establish a timeline that allows for thorough examination, data collection, and collaborative decision-making. This measured approach ensures that improvements are well-planned and sustainable.
- Training and Skill Development:
Invest in training programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of employees involved in the VSM process. Equip team members with the necessary tools and techniques to conduct value stream mapping effectively. This investment in skill development ensures that the organization has a capable and empowered workforce capable of driving continuous improvement initiatives.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the Vector Space Model (VSM)?
A1: The Vector Space Model (VSM) is a mathematical model used in information retrieval to represent text documents as vectors in a multidimensional space. It is commonly employed in natural language processing and text mining applications.

Q2: What are some key applications of VSM?
A2: VSM is widely used in information retrieval, document similarity analysis, text classification, and clustering. It plays a crucial role in tasks such as document retrieval, text summarization, and recommendation systems.
Q3: What are the best practices for preprocessing text data before applying VSM?
A3: Before using VSM, it’s essential to preprocess text data. This involves steps such as lowercasing, removing stop words, stemming or lemmatization, and handling special characters. Cleaning and standardizing the text data contribute to better vector representations.
Q4: How do I choose the right vectorization technique in VSM?
A4: The choice of vectorization technique depends on the specific task and dataset. Common methods include TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) and word embeddings (e.g., Word2Vec or GloVe). Experiment with different techniques and evaluate their impact on your specific use case.
Q5: How can I handle the issue of word order in VSM?
A5: VSM typically disregards word order. To address this, consider using techniques like n-grams or exploring more advanced models, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or transformers, which can capture sequential dependencies in text.
Q6: Is dimensionality reduction recommended in VSM? A6: Yes, dimensionality reduction techniques, such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) or Truncated Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), can be beneficial in managing the high-dimensional nature of vector spaces. They help in reducing computational complexity and noise in the data.
Q7: How do I evaluate the performance of a VSM-based model?
A7: Evaluation metrics depend on the specific task. For document similarity, metrics like cosine similarity or Euclidean distance can be used. In classification tasks, accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score are commonly employed. Cross-validation is also recommended to assess generalization performance.
Q8: What are some considerations for updating VSM representations over time? A8: In dynamic environments, it’s crucial to update VSM representations periodically. This can be achieved by retraining the model with new data or incorporating incremental learning techniques. Ensure that the model adapts to changes in the underlying data distribution.
Q9: Can VSM handle multiple languages?
A9: VSM can be extended to handle multiple languages. However, it’s important to use language-specific preprocessing techniques and consider language embeddings or multilingual embeddings for improved representation of text in different languages.
Q10: Are there any resources for further learning about VSM best practices?
A10: Yes, there are various resources, including research papers, online courses, and tutorials. Some recommended readings include “Introduction to Information Retrieval” by Manning, Raghavan, and Schütze, and online platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses on natural language processing and text mining that cover VSM concepts in-depth.
Conclusion:
Value Stream Mapping remains a potent tool for organizations striving to optimize their processes and deliver greater value to customers. By adhering to these VSM best practices, businesses can streamline operations, reduce waste, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. As technology advances and markets evolve, embracing the principles of VSM becomes increasingly critical for organizations seeking to thrive in the dynamic and competitive landscape of today’s business world.